Adult learners Technology Presentation
Combining ER and distant reading using literary texts with computer coding
With the development of Gutenberg's printing technology, the number of publications increased in large numbers, and the purpose of reading and the way of reading diversified. Then, with the advent and development of digital technology such as computers, not only paper books but also digital books have increased. In the meantime, the way of reading has become more diverse. Among several reading methods, extensive reading (ER) is still a useful method, but in some cases, it needs to be used properly with other reading methods in the era of big data. Among other types of reading, there is distant reading (DR). DR is a term coined by Franco Moretti, an Italian literary scholar, to describe a methodology of literary analysis that involves the quantitative analysis of large amounts of literary texts. In this presentation, we would like to introduce a teaching method that can properly combine ER and DR for literary texts. For DR, beginner-level computer coding activities are covered in this presentation. The programming language for DR is R. R is well-liked and widely used among professionals who work with data, particularly those who specialize in data science. In this presentation, we also introduce a checklist and materials for the ER-DR classes.
-

Youngwoo Kim is a lecturer and researcher at Seoul National University and a visiting professor at the Department of English Language and Literature at Myongji University in South Korea. He researches the use of artificial intelligence in language education and enjoys working with language data. He also enjoys learning and sharing new technologies.
-

Hyunkee Ahn is a professor at Department of English Language Education, Seoul National University, Republic of Korea. His research area includes Applied Phonetics, L2 Phonology & Speaking Assessment. He recently enjoys learning AI-based technologies like automatic speech recognition.
-

Yongkook Won is a lecturer and researcher at Seoul National University and the International Graduate School of English. He teaches courses on AI-based language education and big data analysis. His recent research focuses on investigating fairness in language testing, designing algorithms for automated essay and speaking assessment, and enhancing language teaching and learning through AI-based language learning tools.
-

Kwanghyun Park is a professor at Myongji University, Korea. His research interests include computational processing of learners' texts, automatic writing assessment, and understanding learners' development through text processing.
-

Jung-Hye Choi is an adjunct professor at Duksung Women's University in Seoul, South Korea. Her research area includes Gamification in Literacy Education, Language Learning eXperience (LLX) Design, Game-based Language Learning, Technology-assisted Language Learning and Teacher Education. She recently enjoys Edutech English contents development and AI-based language learning.
-

Joohae Kim is a professor at The Cyber University of Korea. Her research interests include e-Learning, language testing, and AI-assisted language learning.
ER and Language Data Activities
1. Choose a book and read it
1.1. Choose a book to read. An out-of-copyright book is preferable. Sample: Jane Eyre: An Autobiography by Charlotte Brontë
1.2. Obtain the book to read. For ebooks, get the file. Sample: Jane Eyre at Project Gutenberg (https://www.gutenberg.org/ebooks/1260)
1.3. Read the book. For Kindle: https://www.amazon.com/gp/help/customer/display.html?nodeId=G5WYD9SAF7PGXRNA
1.4. Consider using a reading tracking app to record your book reading activity. Ex: Goodreads, StoryGraph, etc.
2. Utilize the book's text data
2.1. Obtain an Excel file with the book's text data. Sample: JaneEyre_Results_Text.xlsx
2.2. Handle the Excel file in a computer. Or use Google Sheets.
2.3. Utilize Excel's features: Searching, sorting, tabulation, etc.
3. Mining the text
3.1. Obtain the text data of the book as a text file. An excel file will do. Sample: JaneEyre.txt (in the Posit Cloud project)
3.2. Prepare a coding environment. For R, create an account at Posit Cloud (https://posit.cloud/)
3.2. Obtain text mining code written in R. Sample: https://posit.cloud/content/6256020
3.3. Mine text of the book with codes provided.
3.4. Utilize the text mining results (excel file, visuals, etc.) for your reading activity.
Demonstration Video (Please copy the link, if it doesn't work)
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=MI_3fYgqNtQ
Contact: youngwoolearning@gmail.com (Youngwoo KIM, presenter)
Visualizations from text mining j_top20_wordcloud.jpg 212.62 KB
j_top20_wordcloud.jpg 212.62 KB g_sentiment_bargraph.png 40.85 KB
g_sentiment_bargraph.png 40.85 KB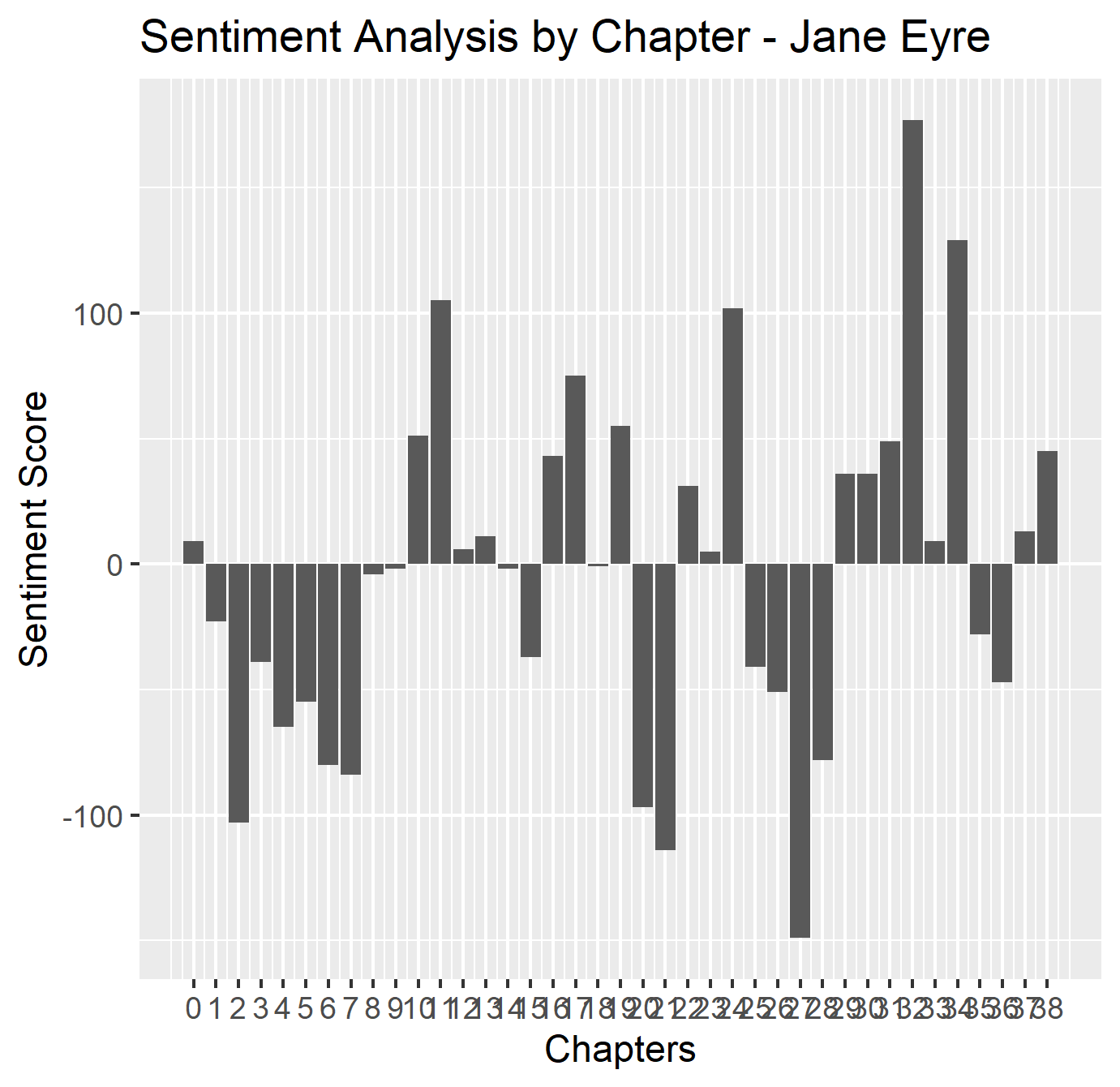 j_sentiment_bargraph_chapter.png 34.28 KB
j_sentiment_bargraph_chapter.png 34.28 KB j_network_bigrams.jpg 174.83 KB
j_network_bigrams.jpg 174.83 KB l_top20_wordcloud.jpg 241.87 KB
l_top20_wordcloud.jpg 241.87 KB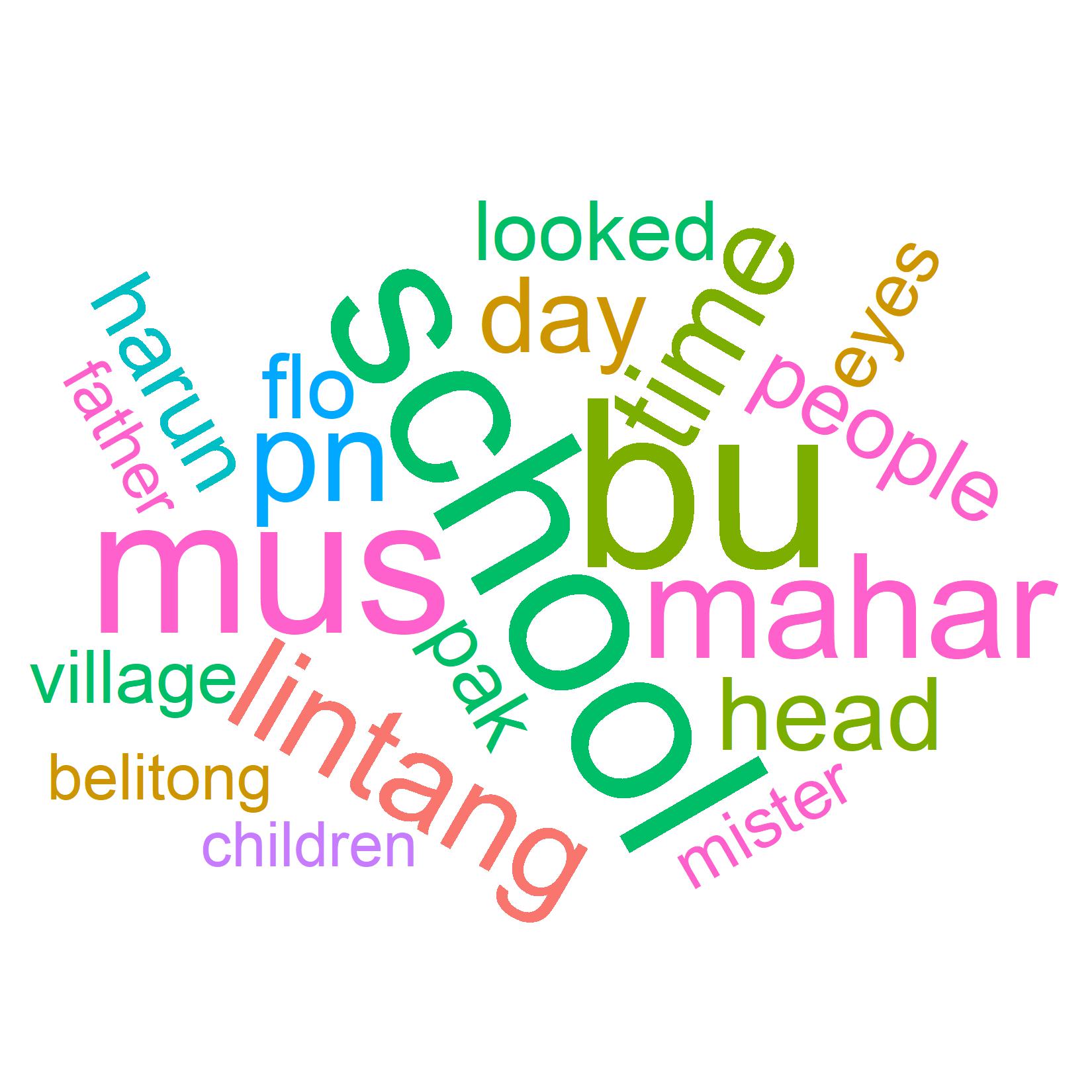 t_top20_wordcloud.jpg 182.72 KB
t_top20_wordcloud.jpg 182.72 KB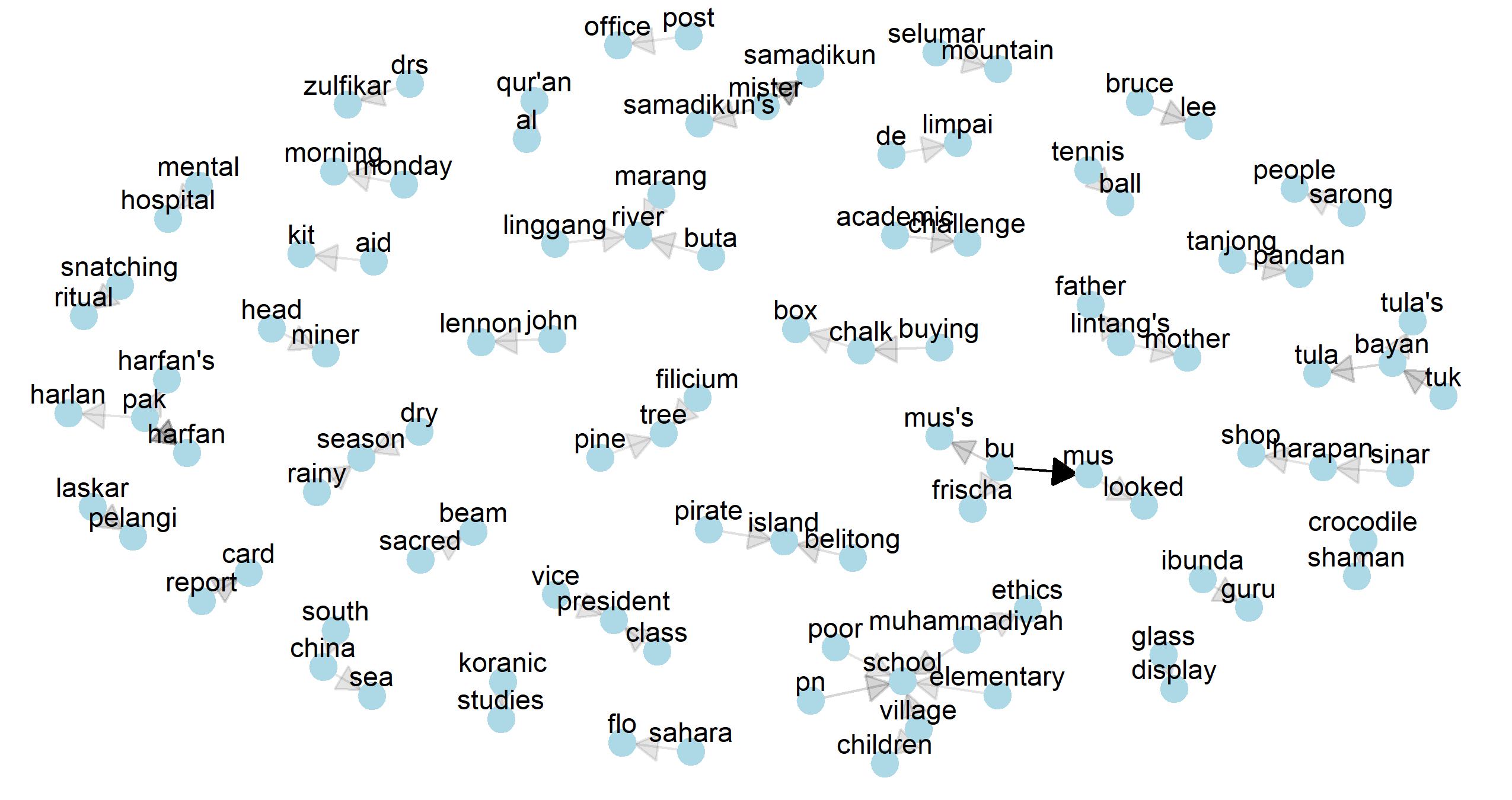 t_network_bigrams.jpg 266.01 KB
t_network_bigrams.jpg 266.01 KB